Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can vary in size and cost, and they can involve a single research center or multiple centers, in one country or in multiple countries. Clinical study design aims to ensure the scientific validity and reproducibility of the results.
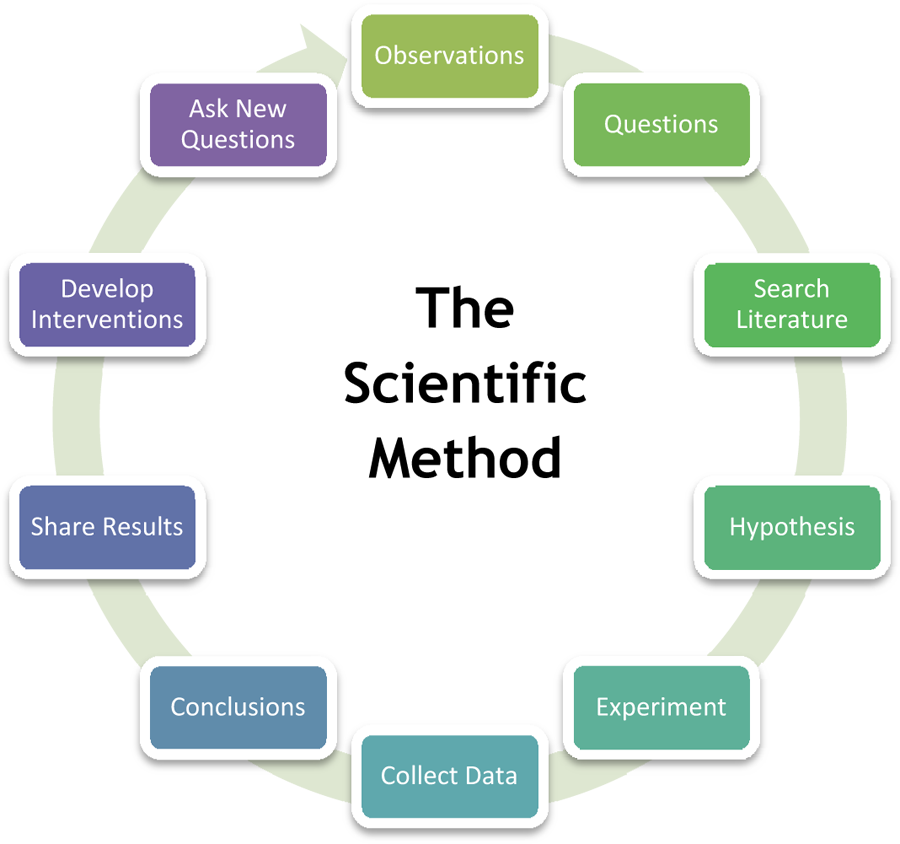
Scientific research can be subdivided into different classifications according to their academic and application disciplines. Scientific research is a widely used criterion for judging the standing of an academic institution, but some argue that such is an inaccurate assessment of the institution, because the quality of research does not tell about the quality of teaching (these do not necessarily correlate). Generally, research is understood to follow a certain structural process. Though step order may vary depending on the subject matter and researcher, the following steps are usually part of most formal research, both basic and applied:
Observations and formation of the topic: Consists of the subject area of one's interest and following that subject area to conduct subject-related research. The subject area should not be randomly chosen since it requires reading a vast amount of literature on the topic to determine the gap in the literature the researcher intends to narrow. A keen interest in the chosen subject area is advisable. The research will have to be justified by linking its importance to already existing knowledge about the topic.
Hypothesis: A testable prediction which designates the relationship between two or more variables.
Conceptual definition: Description of a concept by relating it to other concepts.
Operational definition: Details in regards to defining the variables and how they will be measured/assessed in the study.
Gathering of data: Consists of identifying a population and selecting samples, gathering information from or about these samples by using specific research instruments. The instruments used for data collection must be valid and reliable.
Analysis of data: Involves breaking down the individual pieces of data to draw conclusions about it.
Data Interpretation: This can be represented through tables, figures, and pictures, and then described in words.
Test, revising of hypothesis
Conclusion, reiteration if necessary
Pharmaceutical companies may deal in generic or brand medications and medical devices. They are subject to a variety of laws and regulations that govern the patenting, testing, safety, efficacy using drug testing and marketing of drugs.
Drug discovery is the process by which potential drugs are discovered or designed. In the past, most drugs have been discovered either by isolating the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by serendipitous discovery. Modern biotechnology often focuses on understanding the metabolic pathways related to a disease state or pathogen, and manipulating these pathways using molecular biology or biochemistry. A great deal of early-stage drug discovery has traditionally been carried out by universities and research institutions.
Drug development refers to activities undertaken after a compound is identified as a potential drug in order to establish its suitability as a medication. Objectives of drug development are to determine appropriate formulation and dosing, as well as to establish safety. Research in these areas generally includes a combination of in vitro studies, in vivo studies, and clinical trials. The cost of late stage development has meant it is usually done by the larger pharmaceutical companies. The pharmaceuticals and biotechnology industry spends more than 15% of its net sales for Research & Development which is in comparison with other industries by far the highest share.

Trident Technology LLC provides business solutions and resources to leading business and companies in various sectors.
Many Banking, Financial and Insurance companies provide their customers with website and app to check their financials.
Read More
Trident Technology LLC provides Staffing, Recruiting and many different services at very reasonable cost.
Read More
Trident Technology LLC provides resources and solutions to Government projects.
Read More
Manufacturing is the top sector for US Economy. We provide skilled professionals from different geographical region.
Read More
Retail sector needs digital transformation by taking right resources. We provide resources to your needs for e-commerce applications.
Read More
We help clients stay ahead of their competitors by employing industry specialists having hands-on experience in pharma and life sciences projects.
Read More
Project Done
Happy Clients
Awards
Success Rate